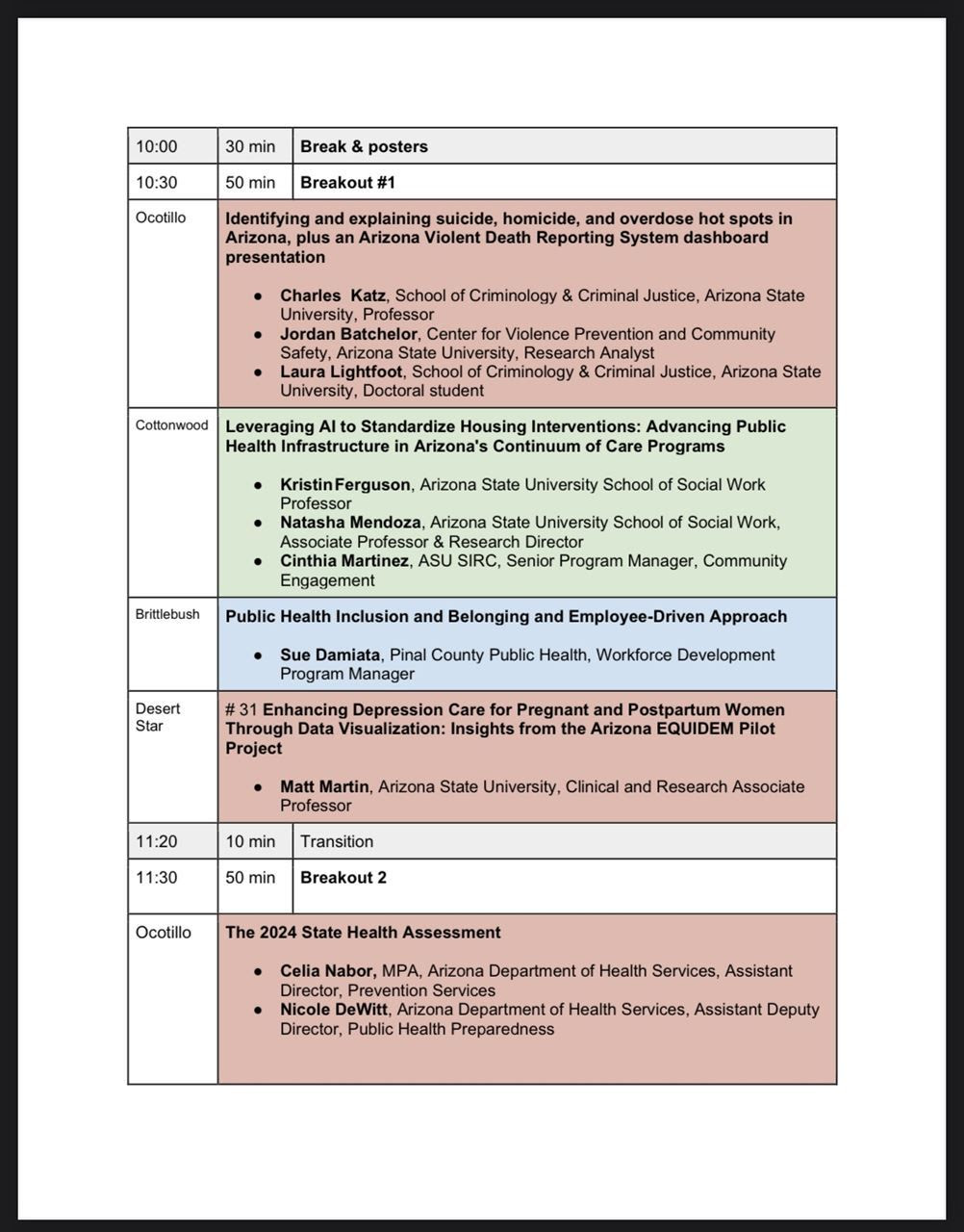
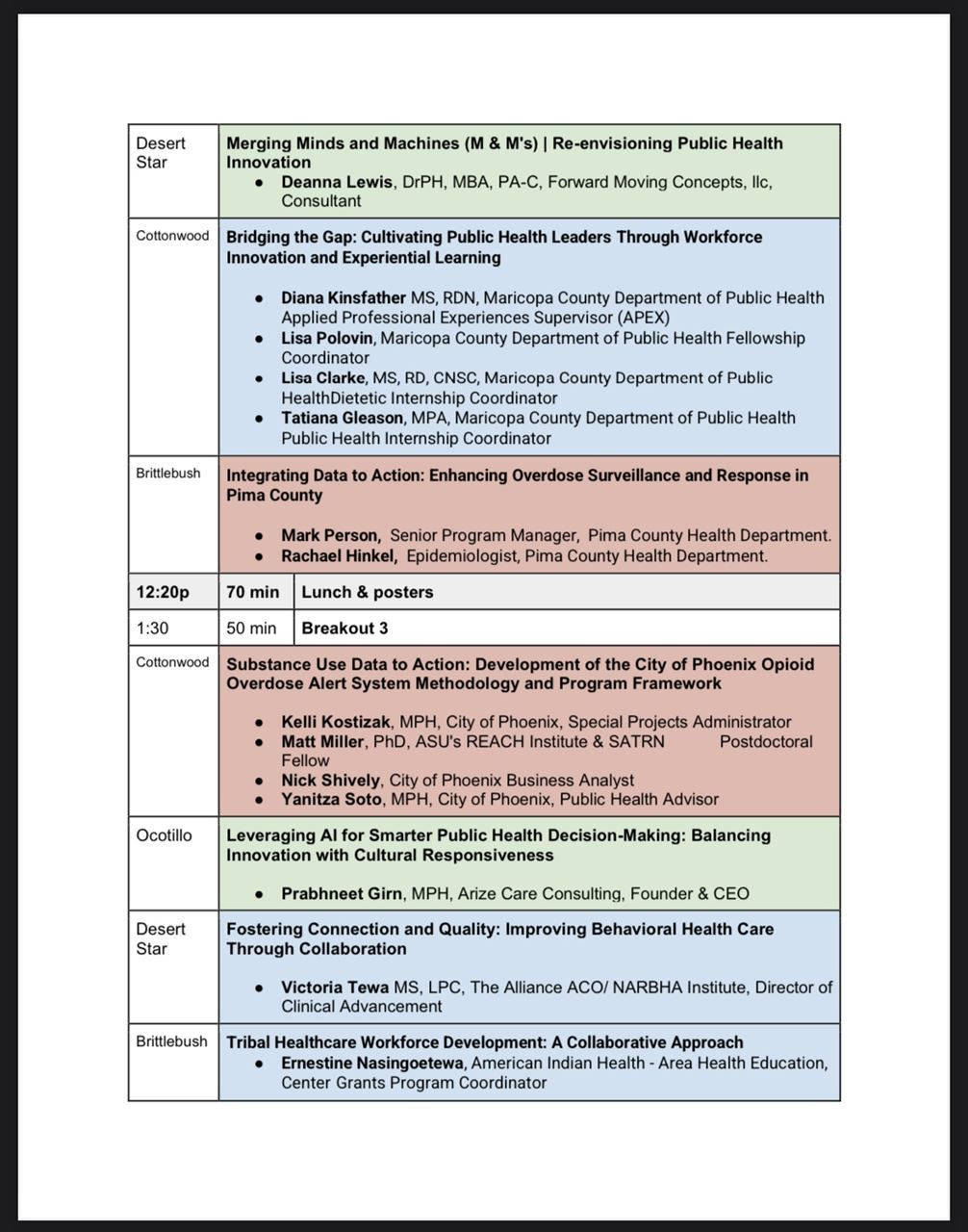
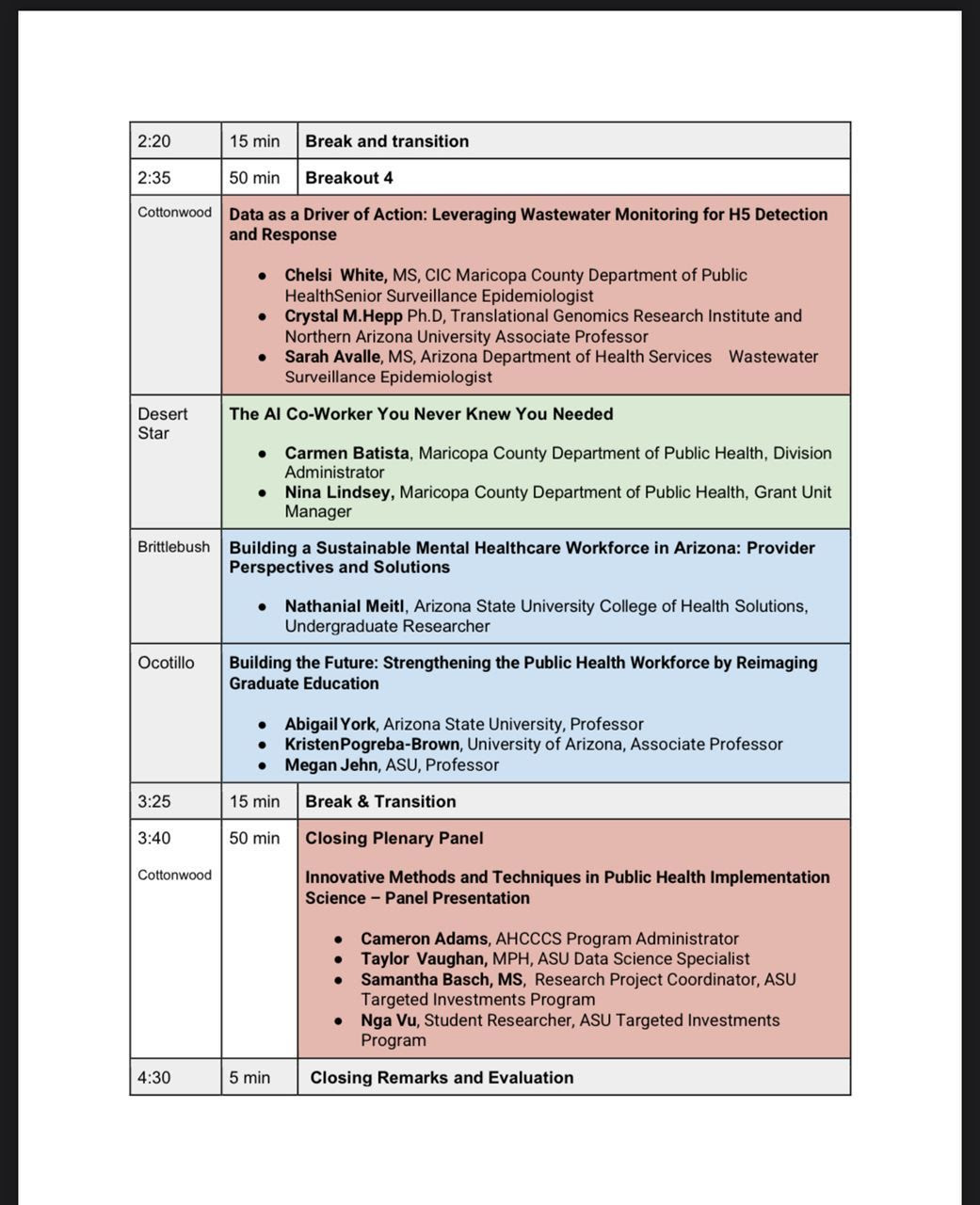
Attorney General Kris Mayes attended the Arizona Center for Rural Health Policy Forum last week and talked about how she and the other 22 democratic attorney generals are fighting the parts of the Project 2025 agenda now being implemented by the Trump Administration that they believe are unlawful or unconstitutional.
As policy decisions are made by the federal agencies or a DOGE bro – the staff at the state attorney general offices examine the decisions, prepare research, and build & file lawsuits to challenge those that conflict with existing federal law or that are unconstitutional.
That work has already bore some fruit. Several lawsuits have been filed about various policy decisions, with several judges issuing preliminary injunctions or temporary restraining orders halting those decisions – at least temporarily.
Here are a few examples:
- Challenge to Birthright Citizenship Executive Order: Multiple federal judges have issued preliminary injunctions blocking the enforcement of President Trump’s executive order aimed at ending birthright citizenship. These rulings assert that the order likely violates the Fourteenth Amendment.
- Lawsuit Against Federal Funding Freeze: A coalition of 23 states, filed motions resulting in a federal judge issuing a temporary restraining order against the Trump administration’s freeze on federal grants and loans. The court found the funding freeze to be potentially unlawful and issued a TRO.
- Legal Challenge to “Fork in the Road” Directive: A federal judge extended a temporary restraining order against the Trump administration’s “Buy Out, Fork in the Road Directive,” which aimed to alter government procurement processes. The extension prevents the directive’s implementation pending further legal review.
- Opposition to DEI and Gender-Related Executive Orders: Civil and human rights organizations filed a lawsuit challenging executive orders targeting Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion initiatives and gender identity policies. The plaintiffs argue these orders violate constitutional rights, leading to ongoing legal proceedings (no judge decision as of yet).
- Litigation Over USAID Funding Freeze: A federal judge has ordered the administration to release frozen USAID funds, but the Trump administration has been ignoring that Order leading to ongoing legal challenges and calls for enforcement of the court’s directive (more on this process in the next blog).
- Case Involving Special Counsel Dismissal: Hampton Dellinger, obtained a temporary restraining order preventing his firing by Trump. The case challenges the president’s authority to remove certain federal officials, and has already been escalated to the U.S. Supreme Court for resolution.
The judicial branch of government will be crucial in potentially mitigating some of the dangerous and harmful public health and healthcare decisions being implemented by the Trump Administration.
Some of those cases will ultimately be successful and some won’t – but until the mid-term elections the judicial branch is our most important tool for mitigating the damage.
But… what if Mr. Trump, his secretaries or the DOGE bros ignore those court orders? What’s the remedy?
That’s the topic for my piece tomorrow: Legal Remedies when the Trump Administration Ignores Federal Court Orders